Introduction: A mortgage is a significant financial tool that enables individuals to purchase homes by borrowing money from a lender, typically a bank or a mortgage lender. It’s a complex financial transaction that involves various terms, conditions, and considerations. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the fundamentals of mortgages, including how they work, the different types available, key factors to consider, and the process of obtaining a mortgage.
Understanding Mortgages:
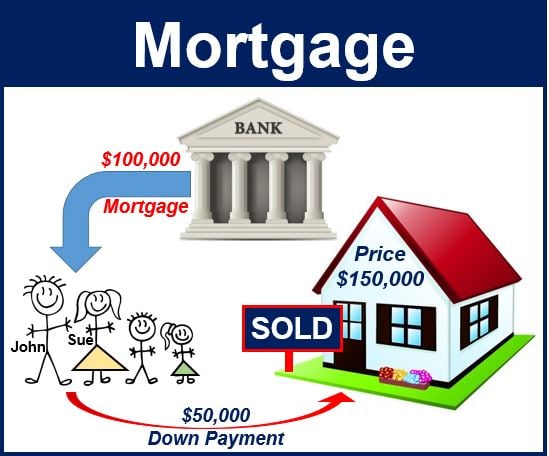
- Definition and Function: A mortgage is a loan secured by real estate property, primarily used to finance the purchase of a home. The borrower (mortgagor) pledges the property as collateral to the lender (mortgagee) until the loan is repaid in full. The mortgage agreement specifies the terms of the loan, including the principal amount, interest rate, repayment schedule, and any additional fees or conditions.
- How Mortgages Work: a. Application and Pre-Approval: The mortgage process begins with the borrower submitting a loan application to the lender, providing financial information, such as income, assets, and credit history. Pre-approval involves the lender evaluating the borrower’s financial profile to determine the maximum loan amount and interest rate they qualify for. b. Property Appraisal: The lender conducts a property appraisal to assess the market value of the home being purchased, ensuring that it serves as adequate collateral for the loan. c. Loan Approval and Closing: Once the loan is approved, the borrower signs a mortgage agreement outlining the terms and conditions of the loan. Closing involves transferring ownership of the property from the seller to the buyer, with the lender funding the loan and the borrower paying closing costs and fees.
Types of Mortgages:
- Fixed-Rate Mortgage (FRM): A fixed-rate mortgage offers a stable interest rate and monthly payment throughout the loan term, typically ranging from 15 to 30 years. It provides predictability and protection against rising interest rates, making it ideal for borrowers who prefer long-term stability and budgeting certainty.
- Adjustable-Rate Mortgage (ARM): An adjustable-rate mortgage features an interest rate that adjusts periodically based on market conditions, typically after an initial fixed-rate period. ARMs offer lower initial interest rates and monthly payments, but they carry the risk of rate increases and payment adjustments over time, making them suitable for borrowers with short-term housing plans or expectations of future income growth.
- Government-Insured Mortgages: Government-sponsored entities such as the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), Veterans Affairs (VA), and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) offer mortgage programs with low down payment requirements and flexible eligibility criteria, making homeownership more accessible to first-time buyers, veterans, and rural residents.
- Jumbo Mortgages: Jumbo mortgages are loans that exceed the conforming loan limits set by government-sponsored enterprises like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. They are used to finance high-value homes and require larger down payments, higher credit scores, and stricter eligibility criteria compared to conventional mortgages.
Pages: 1 2
